[最も人気のある!] model of dna and rna strands 348756-Model of dna and rna strands
Dec 18, DNA consists of two strands, arranged in a double helix These strands are made up of subunits called nucleotides Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, a 5carbon sugar molecule and a nitrogenous base RNA only has one strand, but like DNA, is made up of nucleotides RNA strands are shorter than DNA strandsDNA and rna essential idea The structure of DNA allows efficient storage of genetic information • The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides • DNA differs from RNA in the number of strands present, the base composition and the type of pentose • DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotidesFeb 22, 01a, Top, genomic structureRed and green boxes represent exons in different DNA strands Arrows indicate the origin of transcription on each strand A mutant, mod(mdg4) u1, is shown here that
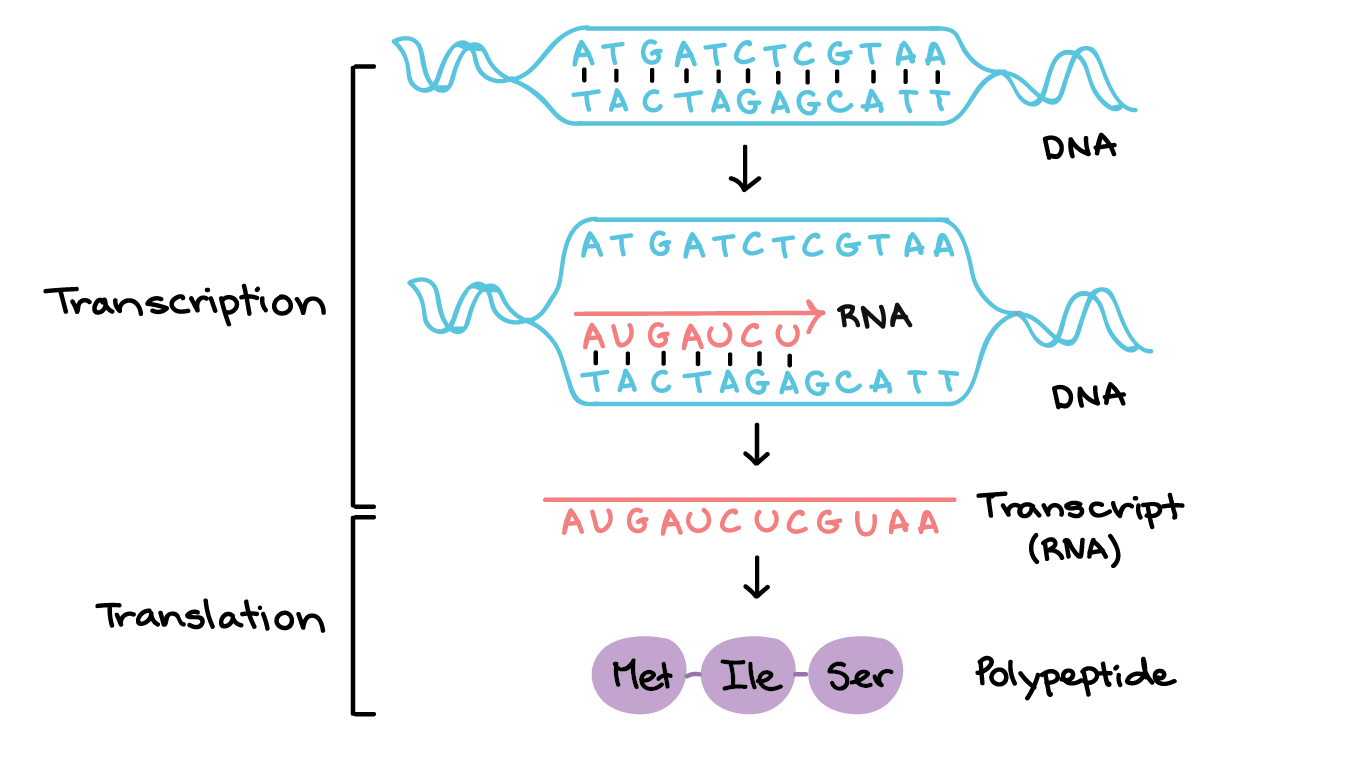
Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy
Model of dna and rna strands
Model of dna and rna strands-Transcription of DNA begins with a bundle of factors assembling at the start of a gene, to read off the information that will be needed to make a protein The blue molecule is unzipping the double helix and copying one of the two strands The yellow chain snaking out of the top is a close chemical cousin of DNA called RNAThe RNA tetrahedrons, the four RNA strands were synthesized by in vitro transcription and then mixed in stoichiometric ratio and annealed in 1×




Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy
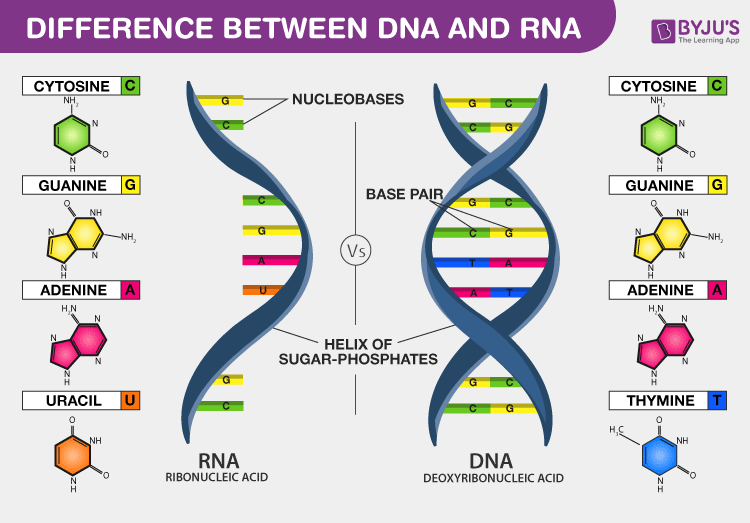
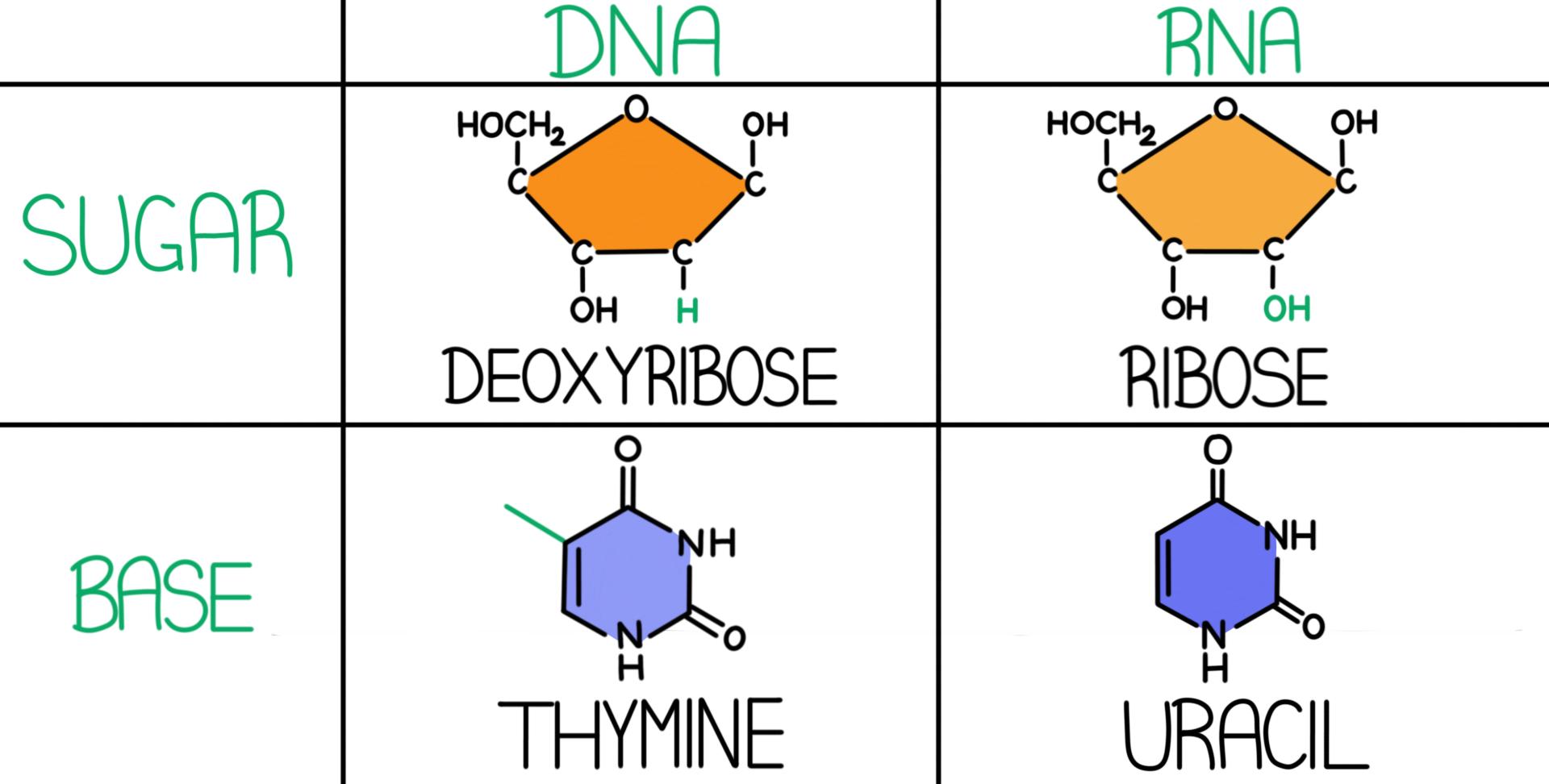
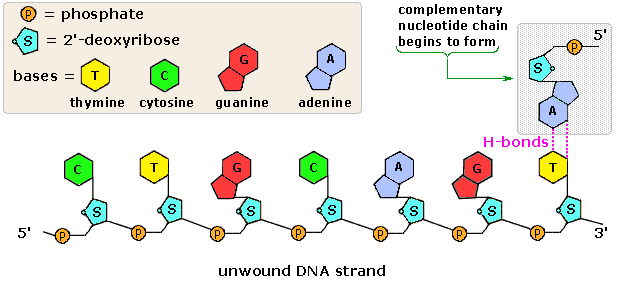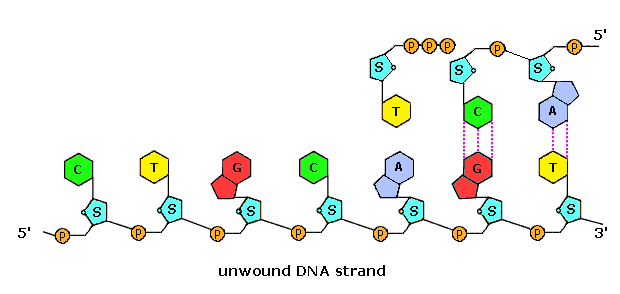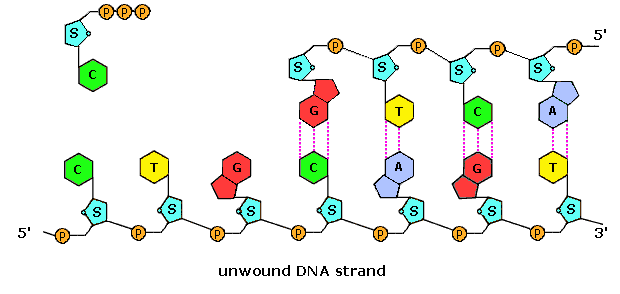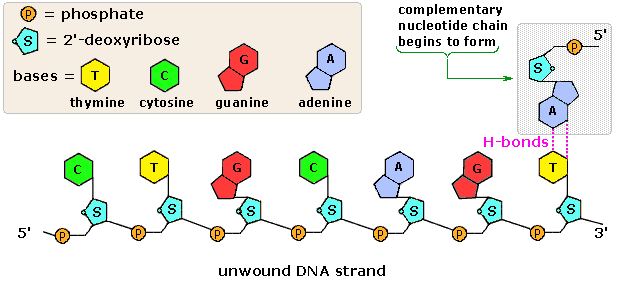
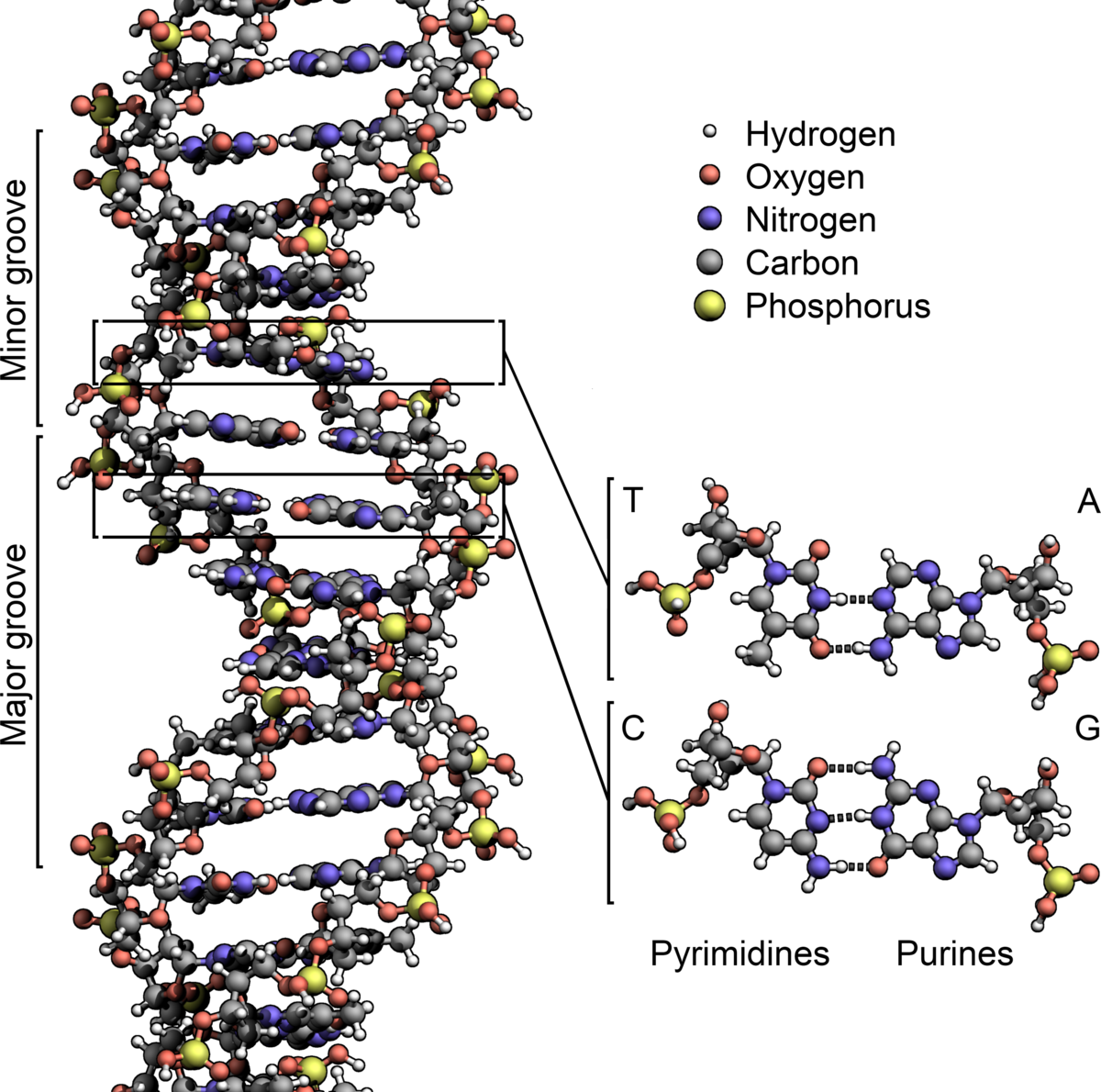
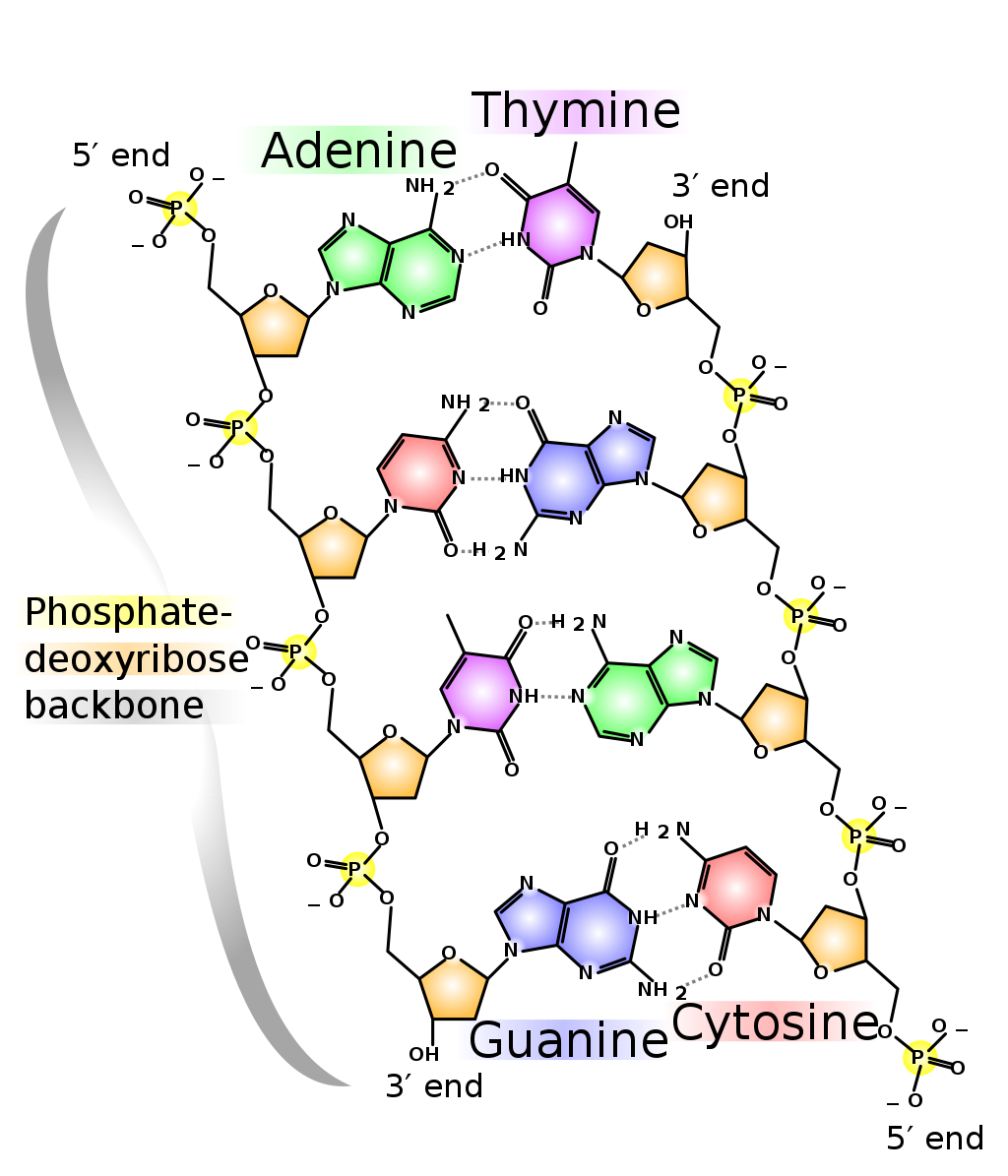
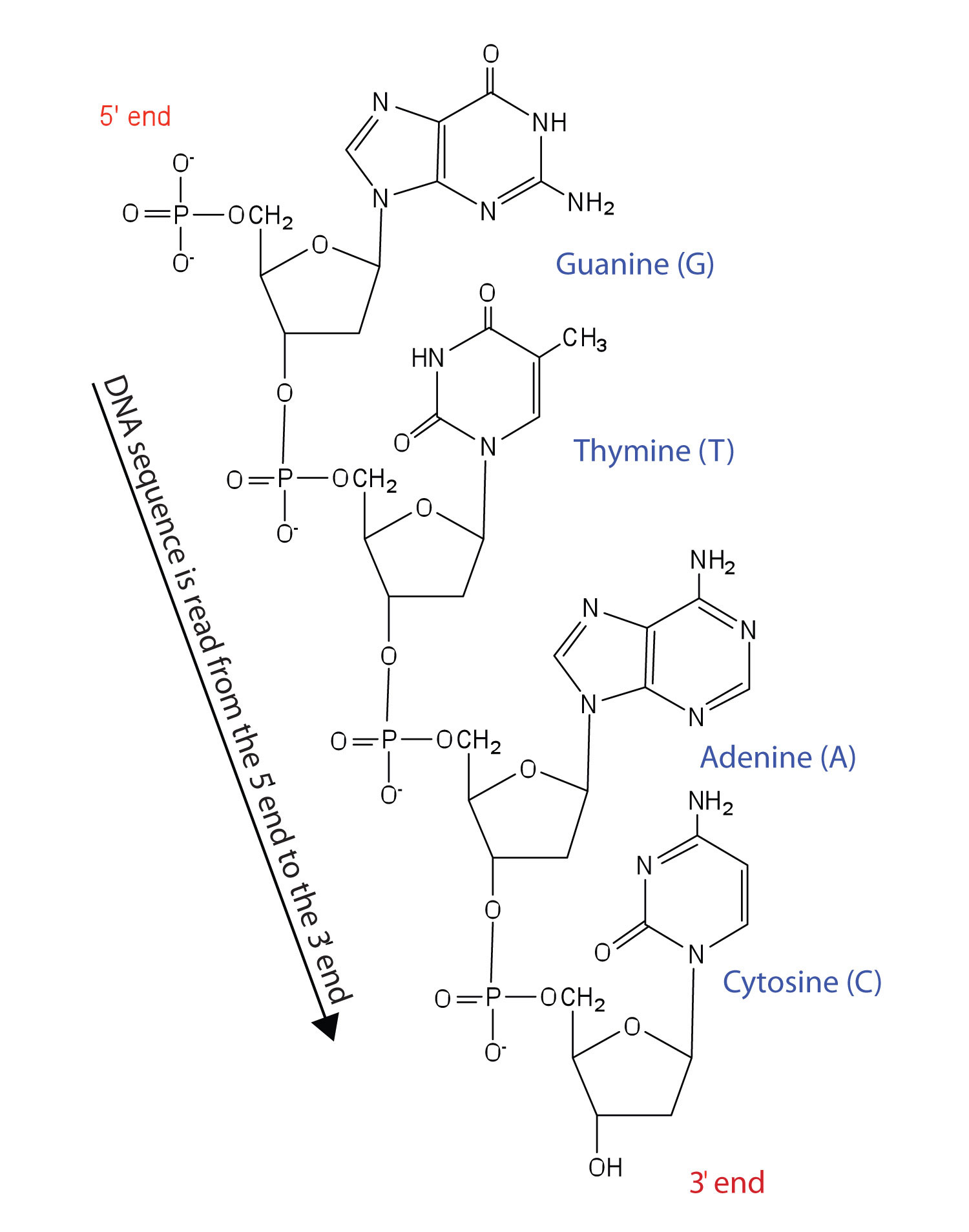
RNA is ribose, and the sugar in DNA is 2'deoxyribose DNA and RNA, though chemically similar, are different in size and have different roles within the cell Molecules of DNA are enormous;That is, the nucleotides were arranged in opposite orientation This can be visualized if the L shape of a nucleotide is imagined to be a sock the neck of the sock is the nitrogenous base, the toe is the phosphate group, and the heel is the sugar groupThe asymmetric ends of DNA strands are referred to as the 5′ (five prime) and 3′ (three prime) ends One of the major differences between DNA and RNA is the sugar, with 2deoxyribose being replaced by the alternative pentose sugar ribose in RNA The four bases found in DNA are adenine (abbreviated A), cytosine , guanine (G) and thymine (T)
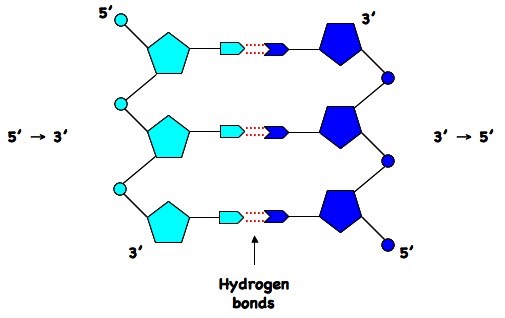
The two strands of Watson and Crick's double helix were antiparallel;Dec 23, But while RNA strands may be good at templating complementary strands, they are not so good at separating from these strands Modern organisms make enzymes that can force twinned strands of RNA—or DNA—to go their separate ways, thus enabling replication, but it is unclear how this could have been done in a world where enzymes didn't yetJun 03, 21The RNA is another nucleic acid that translates genetic information into proteins from DNA The nucleotides are linked together for the formation of two long strands which spiral to produce a structure known as the doublehelix which resembles that of a ladder wherein the sugar and phosphate molecules form the sides while the rungs are formed
Dec 17, Structure of Bacterial DNA (Watson and Crick Model) The bacterial DNA molecule is composed of two strands of complementary nucleotides that are coiled together in the form of a double helix (Fig 61) as described first by Watson and Crick Each strand is composed of three elements It has a backbone of deoxyribose sugar and phosphate groupsMoreover, plasmid DNA formed with the reannealing of individual strands was found to be similar to native plasmid in its properties These findings showed that two strands of a plasmid DNA can be reversibly separated into individual strands and contradicted the Watson and Crick model of DNAThey have molecular weights of up to 1 trillion and are found mostly in the nucleus of the cell Molecules of RNA, by contrast, are much smaller (as low




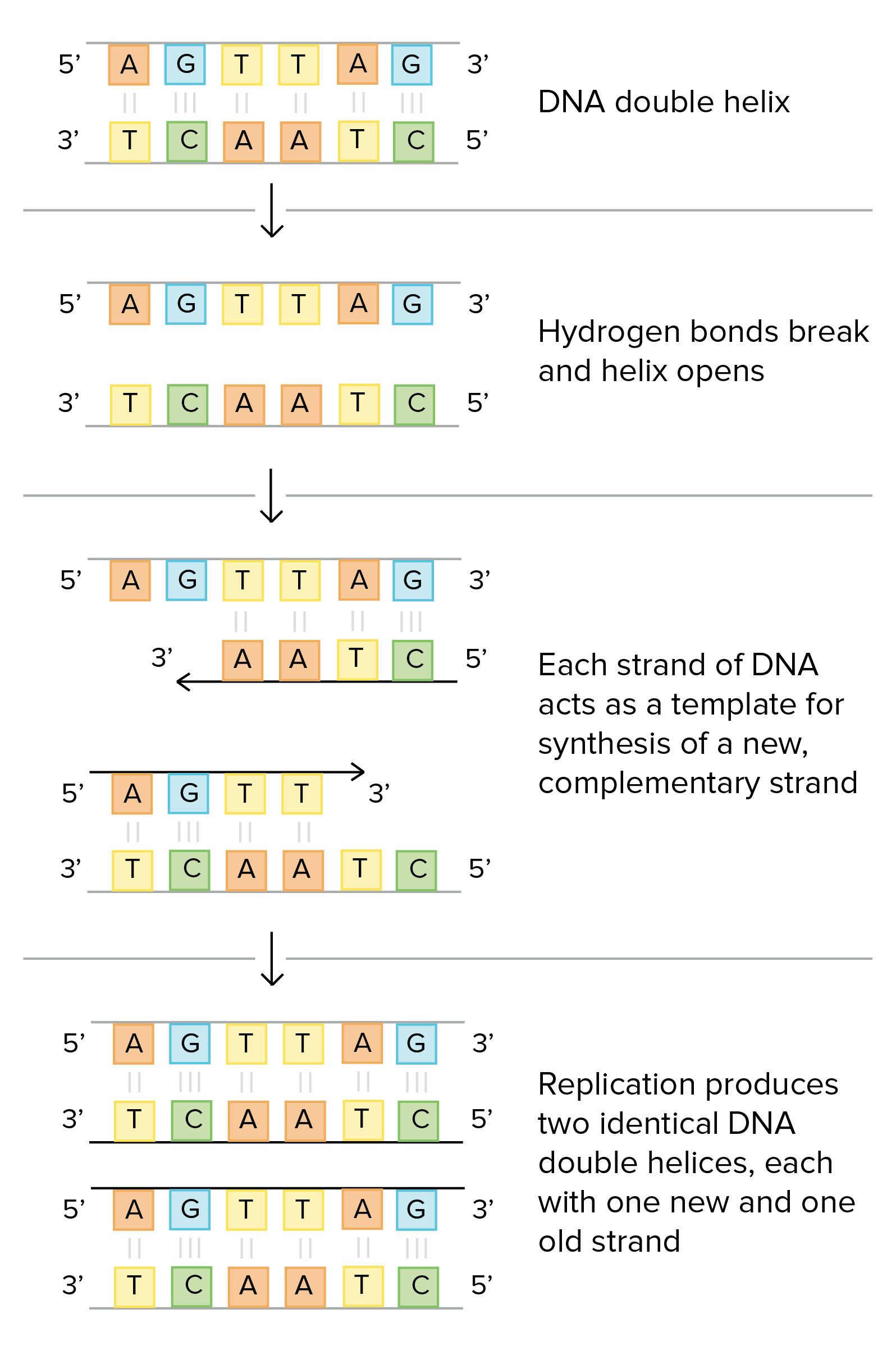
Dna Replication Microbiology



Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy
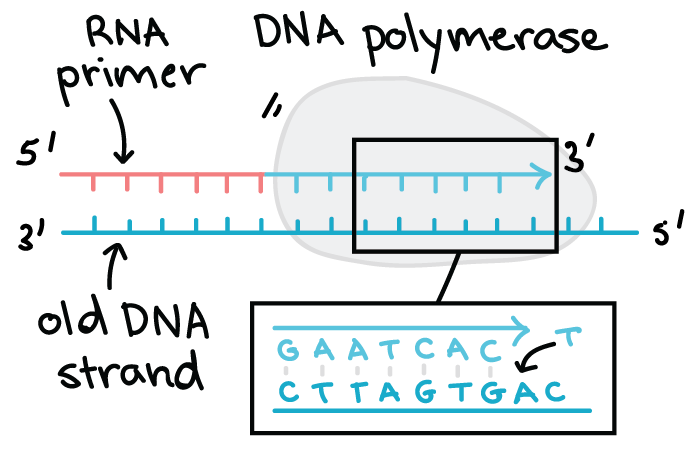
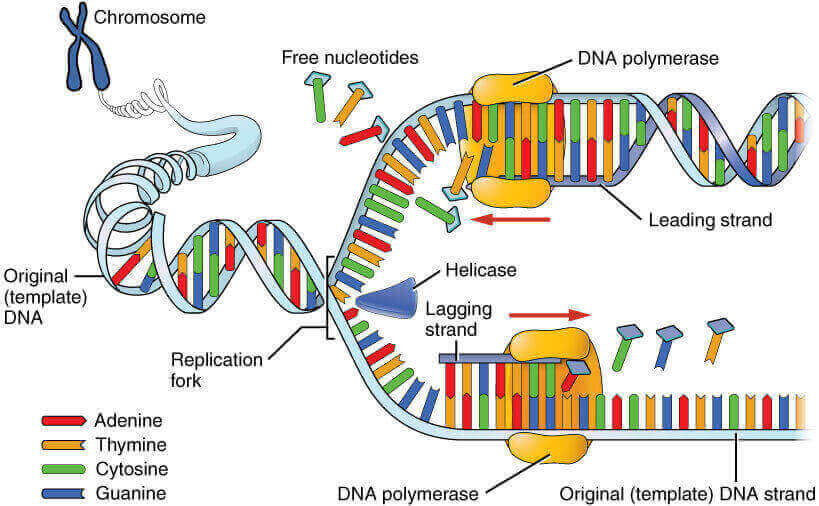
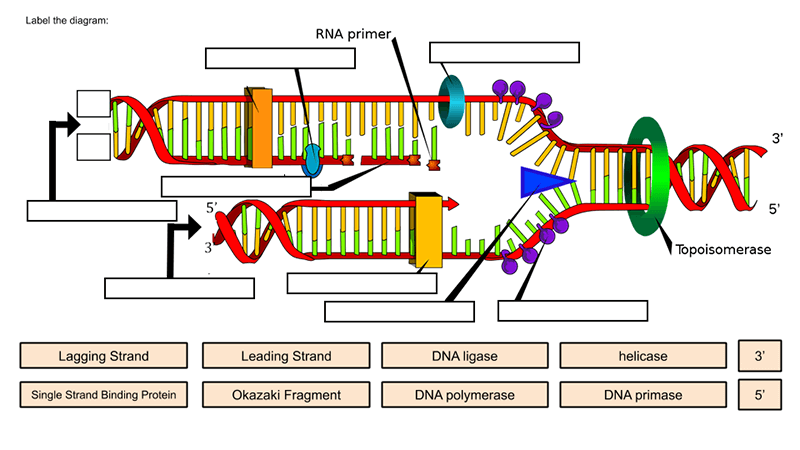
A) RNA primers must be removed and replaced by the deoxynucleotides B) RNA primers must be laid down during DNA replication for synthesis of new DNA that starts at the 3'‑OH of the primer ends C) DNA polymerases can add new nucleotides to either free 3'‑ or‑5'‑end D)Dec 29, "This finding is an important step toward the development of a detailed chemical model of how the first life The researchers claim that "chimeric" strands, made of both RNA and DNADNA LIGASE It reanneals the semiconservative strands and joins OKAZAKI FRAGMENT of the lagging DNA strand PRIMASE It catalyzes the synthesis of a short RNA segment called a "primer" complementary to an ssDNA template 4 What is the trombone model of DNA replication?



Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy



Dna Vs Rna Introduction And Differences Between Dna And Rna
Practice writing a strand of the complementary strand of dna and completing a strand of messenger RNA When you have DNA, adenine pairs with thymine, and cytoEnd Arrows are important when building DNA strands 6 Build a small DNA molecule with just 4 nucleotides A, T, G, and C Your DNA should look like a ladder, with 2 nucleotides on each side of the ladder DIRECTIONS Emphasize the distinction between nucleotides DNA=gray;Dec 15, 17In contrast to the remarkable success of structures selfassembled from multiple components, the progress on designing a singlestranded DNA (ssDNA) or RNA (ssRNA) that can selffold into a defined



Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii




Rna Primer In Dna Replication Definition Function Sequence Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Chromosomal DNA consists of two DNA polymers that make up a 3dimensional (3D) structure called a double helix In a double helix structure, the strands of DNA run antiparallel, meaning the 5' end of one DNA strand is parallel with the 3' end of the other DNA strandTris buffer in a onepot manner Stepwise assembly of the complex was observed by native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) (Figure 1d) The Watson–Crick base paring properties of DNA and RNADNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs 26A1 Crick and Watson's elucidation of the structure of DNA using model making 26S1 Drawing simple diagrams of the structure of single nucleotides of DNA and RNA, using circles, pentagons and rectangles to
/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)



The Differences Between Dna And Rna



Nucleic Acids
In any nucleic acid, RNA or DNA 3' refers to the 3rd carbon of sugar ribose or deoxyribose which is linked to OH group and 5' linked to a triple phosphate group So these 5' and 3' group provide a directional polarity to the DNA or RNA molecule Now a good question would be y26 Structure of DNA and RNA 26U1 The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides 26U2 DNA differs from RNA in the number of strands present, the base composition and the type of pentose 26U3 DNA is double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairsDec 11, 1993For the Pyrimidinepurine* Pyrimidine motif, all eight combinations were tested with each of the three strands composed of either DNA or RNA The chemical nature of sugars has a dramatic influence on triple helix stability For each double helix composition, a more stable triple helix was formed when the third strand was RNA rather than DNA




Dna Replication Biology For Non Majors I




A Model Rna Dna Hybrids To Illustrate The Specificity Of Cleavage At Download Scientific Diagram
May 17, 152 Understandings, Applications and Skills Statement Guidance 26 U1 The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides 26 U2 DNA differs from RNA in the number of strands present, the base composition and the type of pentose 26 U3 DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bondingThe two DNA strands are antiparallel in nature;Watson and Crick model of DNA provides one of the best ways to demonstrate the structure of doublehelix DNAA DNA is a polymer composed by the combination of several monomer units (deoxyribonucleotides) linked by the phosphodiester bondIn the discovery of DNA, many scientists have contextualized the structure of DNA, its components and composition etc



Fact Sheet Dna Rna Protein Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network




The Chemical Structure Of Dna Compound Interest
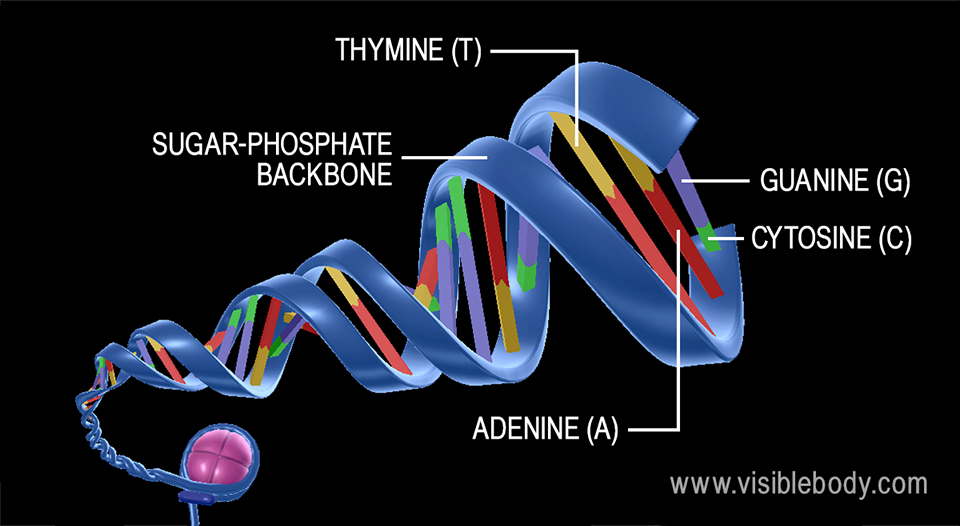
Trombone model of DNA replication in eukaryotic cellRNA= orange Tell students they will not be using the orange RNA today!Apr 21, 17DNA contains the genetic information for the reproduction of life Its structure is that of a twisted double helix that is composed of long strands of alternating sugars and phosphate groups, as well as nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine) The basic unit of structure for a DNA molecule is the nucleotide



3



1
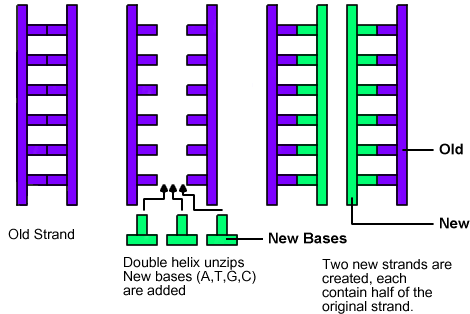
Model reflects the individual structures of DNA and RNA molecules with few to no errors Most components of the backbone and nitrogenous bases are appropriately bonded and accurately represented by different materials and/or colors Weak and strong molecular bonds may beThis video will explain the two different ends of DNA the 3' and 5' ends How these ends are labeled, how to identify them in molecular pictures, and theiDNA and RNA Structure •DNA and RNA are nucleic acids •The model of DNA is like a rope ladder twisted into a spiral – The ropes at the sides represent the sugarphosphate backbones Parental strands Parental strand Daughter strand Two daughter DNA molecules Bubble




Make A Candy Dna Model Stem Activity




Cell Dna The Genetic Material Britannica
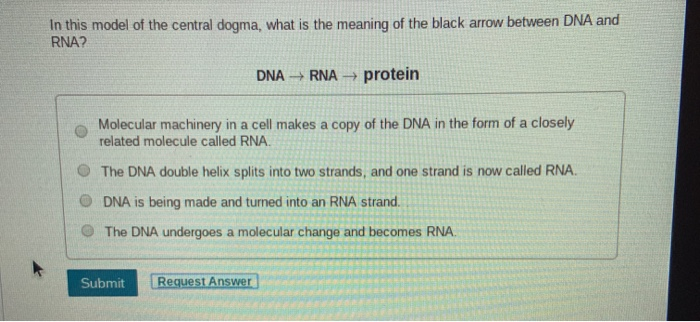
The Watson and Crick model of DNA is a(n)_____ , in which two strands are wound around each other double helix ___________are weak bonds that hold the two strands of DNA together, but also allow the DNA to separate and replicateOnes, now attach to the two free halves creating two strands of DNA Using the other team's model, create two strands of DNA Be sure the bases that attach arc complementary to each other, A to T, and C toG 3Aug 23, The central dogma defines the mechanisms that involve DNA synthesis (replication), RNA synthesis (transcription), protein synthesis (translation), and cDNA synthesis (reverse transcription) Therefore, DNA codes for RNA, RNA codes for proteins, and RNA can also code for DNA in the case of reverse transcription



Dna Structure Bioninja



Dna Structure
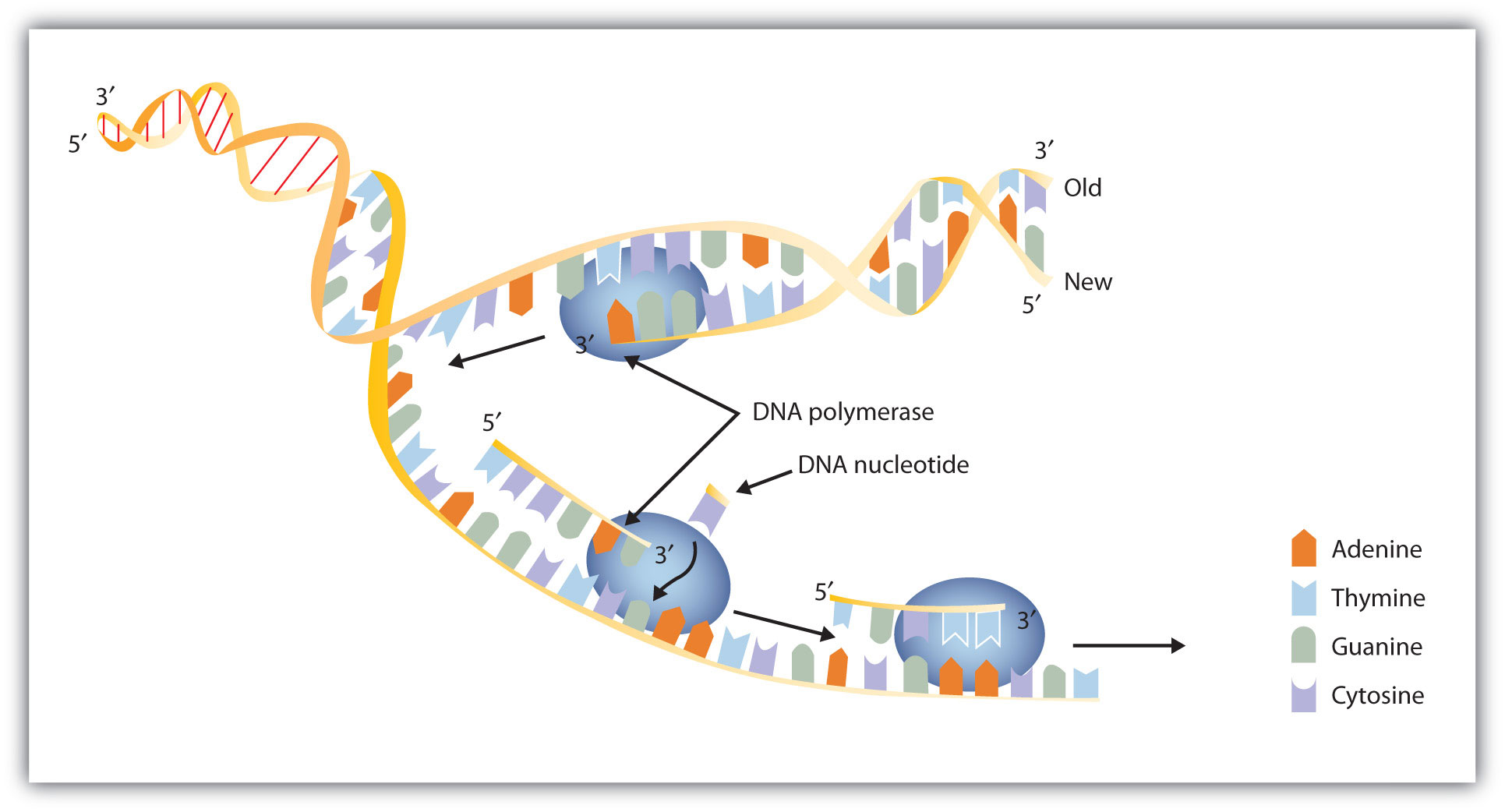
That is, the 3′ end of one strand faces the 5′ end of the other strand The nucleotides that comprise DNA contain a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group which covalently link withFeb 09, 14Structure of Doublehelix Three major forms BDNA ADNA ZDNA BDNA is biologically THE MOST COMMON It is a helix meaning that it has a Right handed, or clockwise, spiral Complementary base pairing • AT • GC Ideal BDNA has 10 base pair per turn(360o rotation of helix) So each base is twisted 36o relative to adjacent bases Base pair are 034 nmFeb 02, Anne Marie Helmenstine, PhD Updated February 02, DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, while RNA is ribonucleic acid Although DNA and RNA both carry genetic information, there are quite a few differences between them This is a comparison of the differences between DNA versus RNA, including a quick summary and a detailed table of the differences




Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy
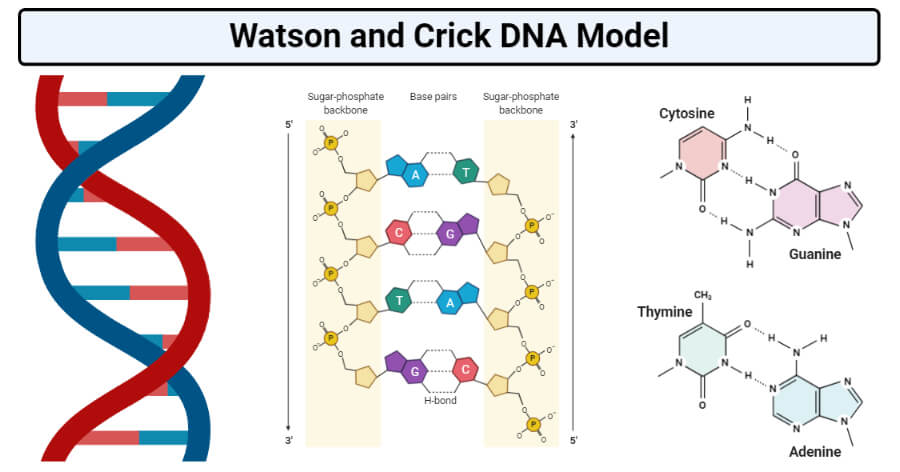



Watson And Crick Dna Model Molecular Biology Microbe Notes
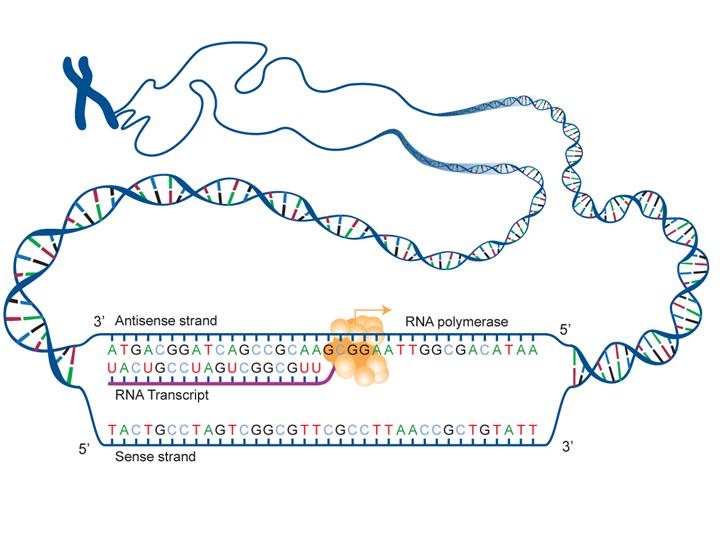
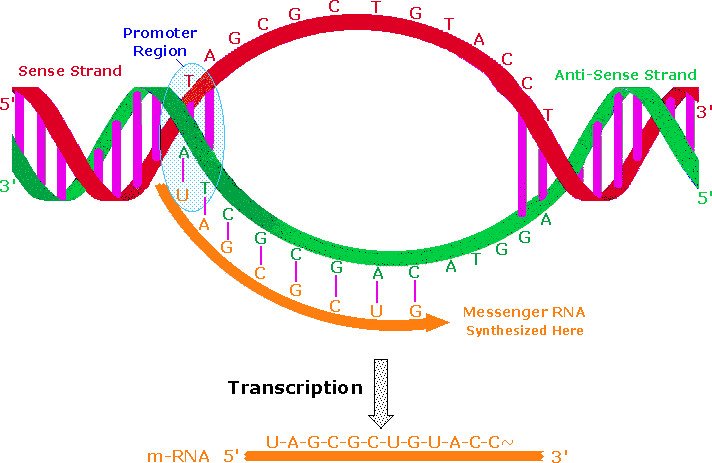
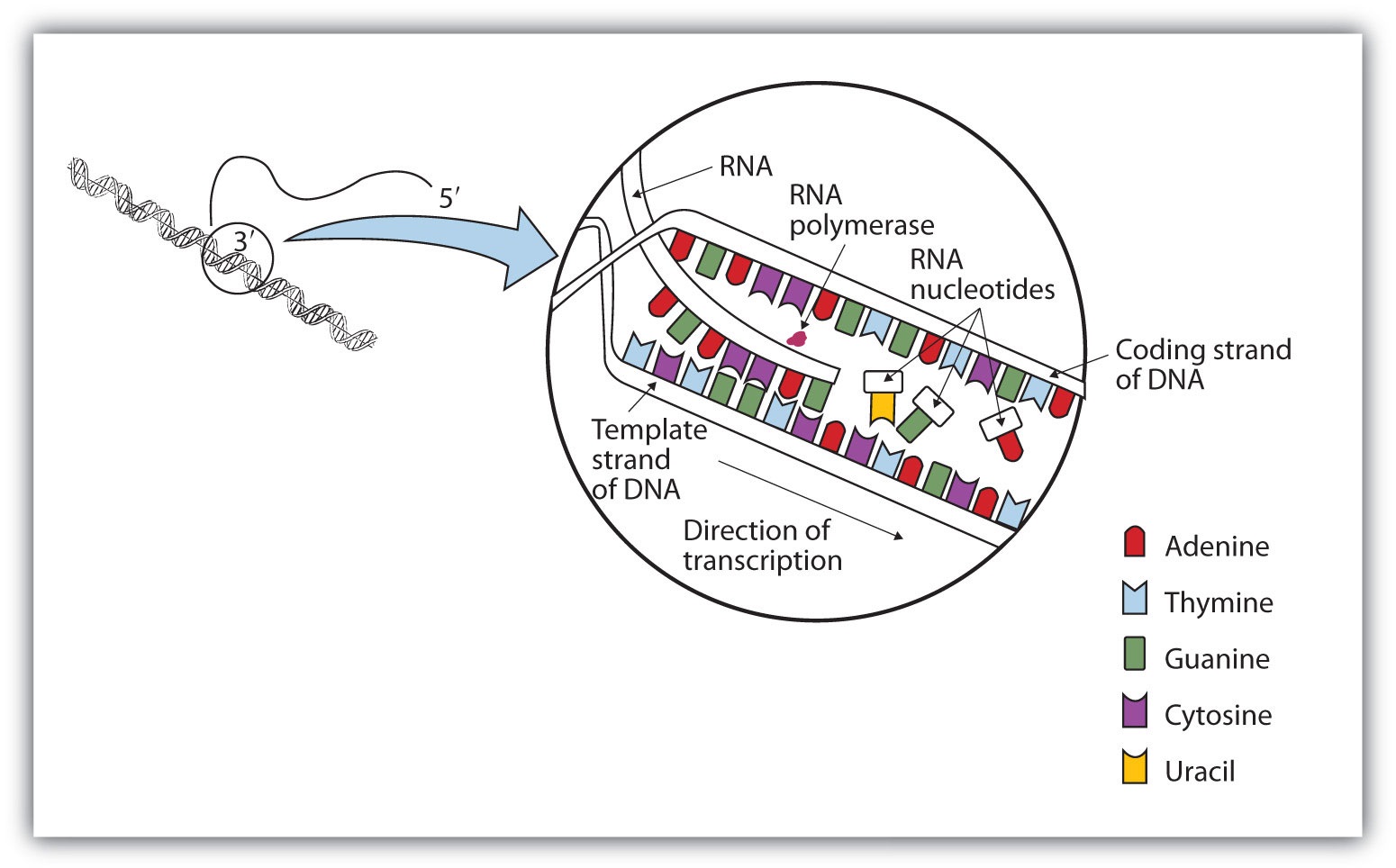
Messenger RNA (mRNA) Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a singlestranded RNA molecule that is complementary to one of the DNA strands of a gene The mRNA is an RNA version of the gene that leaves the cell nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm where proteins are made During protein synthesis, an organelle called a ribosome moves along the mRNA, reads its base sequence, andJan 06, Making DNA models can be informative, fun, and in this case tasty Here you will learn how to construct a DNA model using candy But first, what is DNA?DNA, like RNA, is a type of macromolecule known as a nucleic acid that contains the genetic information for the reproduction of life DNA is coiled into chromosomes and tightly packed in the nucleus of our cellsJan 11, 18DNA is a twostranded molecule that appears twisted, giving it a unique shape referred to as the double helix Each of the two strands is a long sequence of nucleotides or individual units made of




Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable
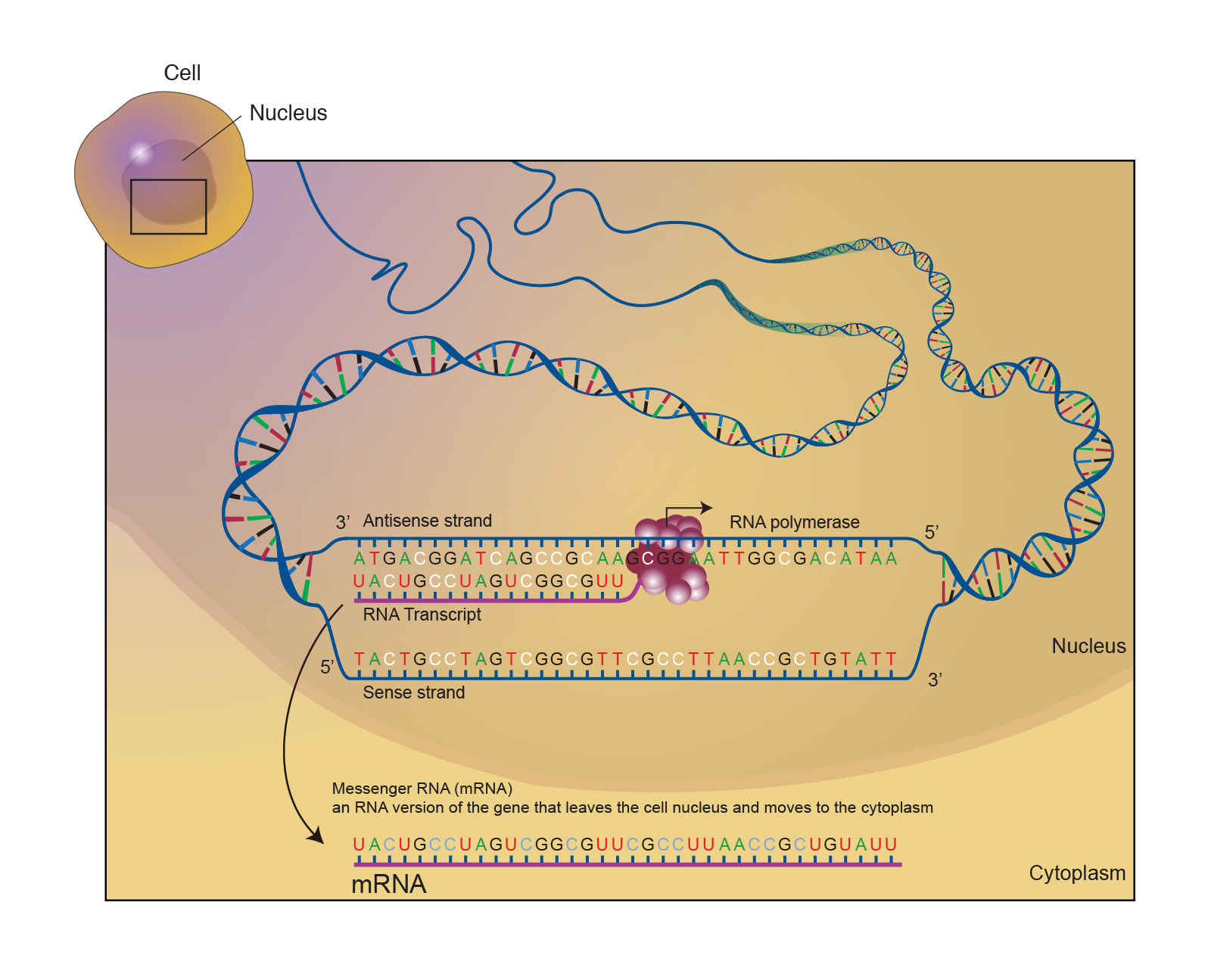



Messenger Rna Mrna
May 14, 15Figure 94 DNA (a) forms a double stranded helix, and (b) adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine (credit a modification of work by Jerome Walker, Dennis Myts) The Structure of RNA There is a second nucleic acid in all cells called ribonucleic acid, or RNA Like DNA, RNA is a polymer of nucleotidesDec 30, DNA vs RNA The chemists behind the new study believe that chimeric strands mixing DNA and RNA molecules fostered replication because they could separate with greater ease Now that we26U2 DNA differs from RNA in the number of strands present, the base composition and the type of pentose 26U3 DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs 26A1 Crick and Watson's elucidation of the structure of DNA using model making




The Acceptor Invasion Model A Minus Strand Dna Blue Line Is Download Scientific Diagram




Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii
Nov 26, 13Types of DNA DNA duplex model proposed by Watson and Crick is right handed spiral and is called BDNA (Balanced DNA) In the model the base pairs lie at nearly right angles to the axis of helix (Fig 65 D) Another right handed duplex model is ADNA (Alternate DNA) Here, a single turn of helix has 11 base pairs2 Observe your two separate strands Note that when the DNA molecule splits in tow, new bases, complimentary to the originalRNA strands are created using DNA strands as a template in a process called transcription, where DNA bases are exchanged for their corresponding bases except in the case of thymine (T), for which RNA substitutes uracil (U) Under the genetic code, these RNA strands specify the sequence of amino acids within proteins in a process called translation
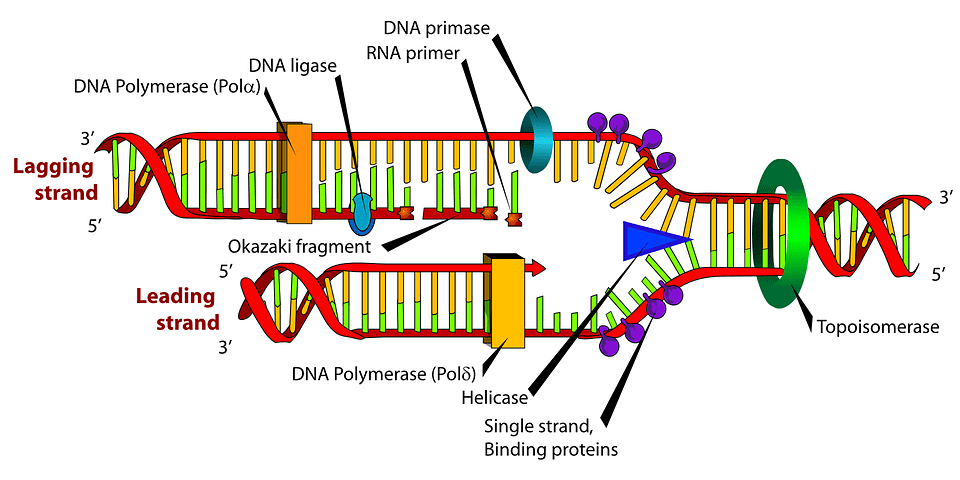



Models Of Dna Replication Notes With Definition Diagram Readbiology Com
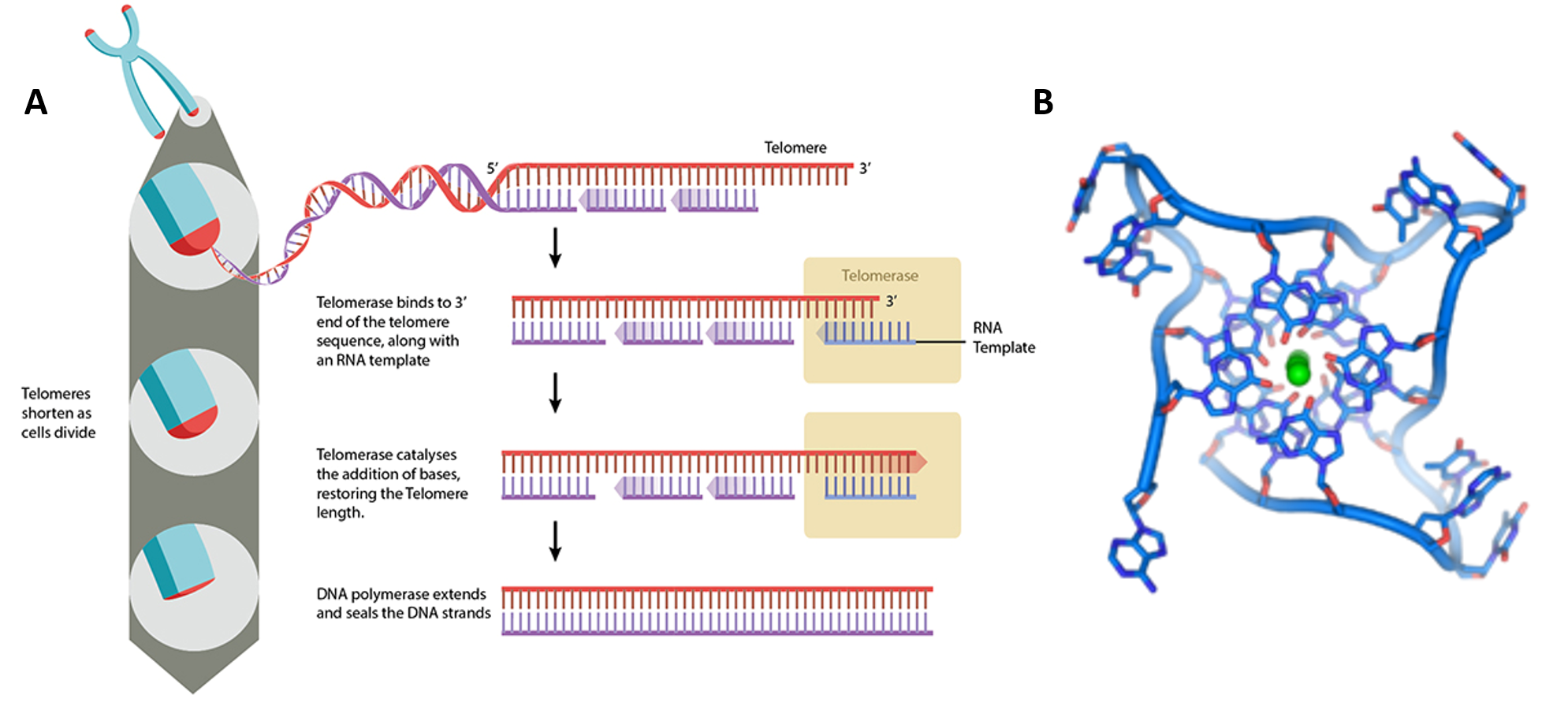



Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry




Kinetic Analysis Of Dna And Rna Strand Transfer Reactions Catalyzed By Vaccinia Topoisomerase Journal Of Biological Chemistry



9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition




Dna 3d Model Dna Model Dna Project Dna Model Project
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/transcription-factor-and-ribosomal-rna-185759536-5be335b9c9e77c005147e9ec.jpg)



Steps Of Transcription From Dna To Rna




Heredity Structure And Composition Of Dna Britannica




Dna Model Science Lab Biology Classroom Supplies Amazon Com Industrial Scientific
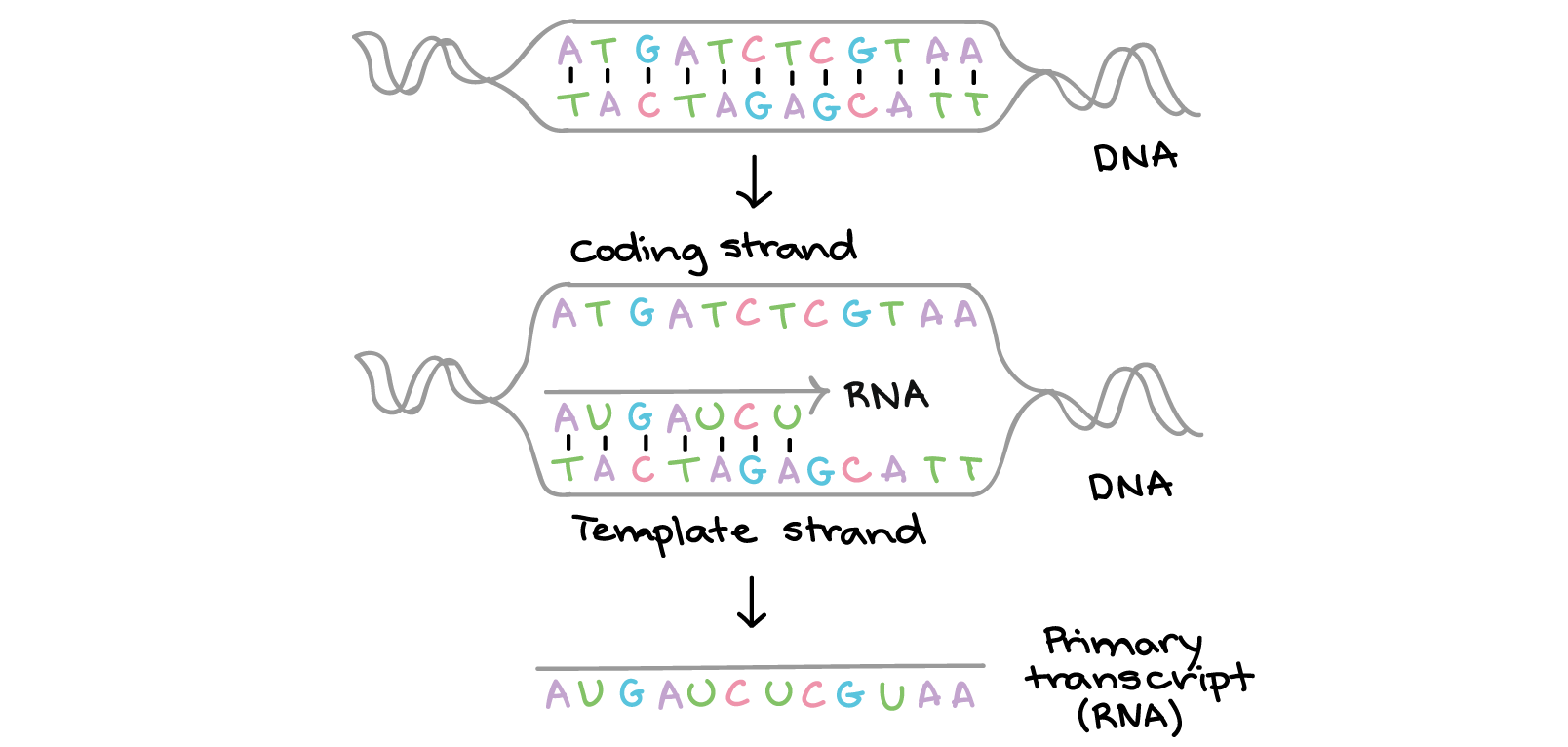



Molecular Genetics High School Biology Science Khan Academy




Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education



Dna Model Replication And Rna Transcription Karina S Blog




Flow Of Genetic Information Kit C
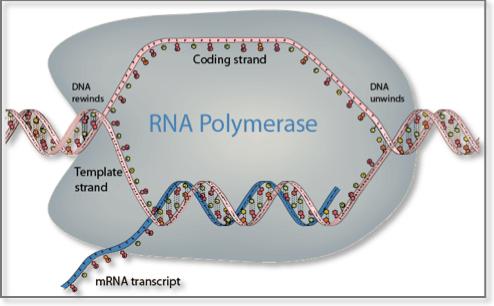



Dna And Rna Computational Medicine Center At Thomas Jefferson University




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna
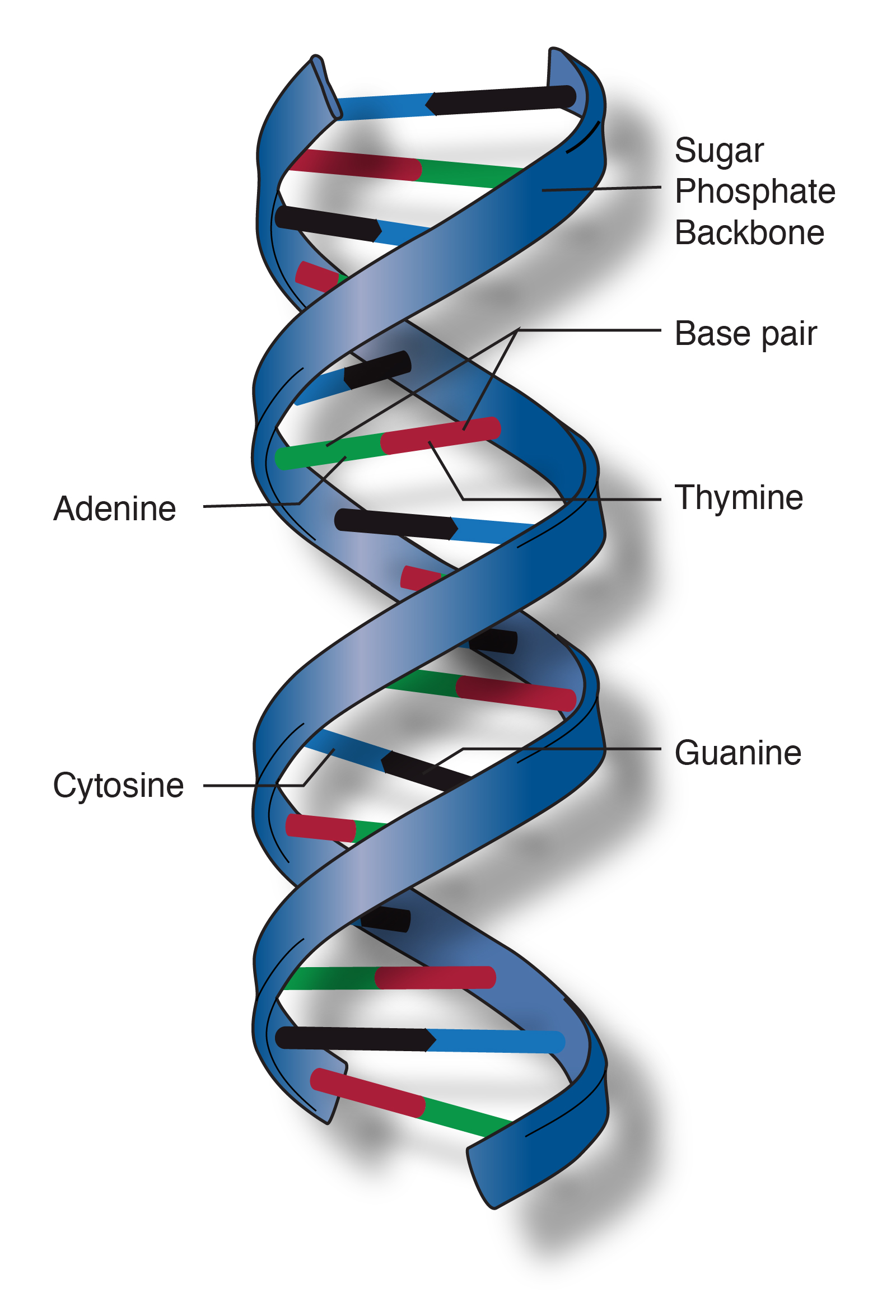



Dna Double Helix




Dna Vs Rna Biology Dictionary
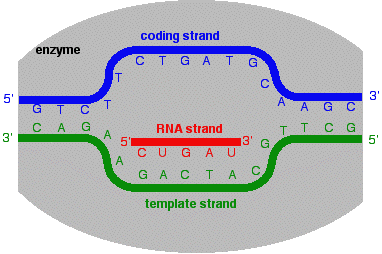



Transcription From Dna To Rna



Nucleic Acids



Dna Replication Explained With Zipper Model Epomedicine



Structure Of Dna And Rna




A Dna Rna Hybrid Complex Model With E Coli Rnase H The Ribbon Model Download Scientific Diagram
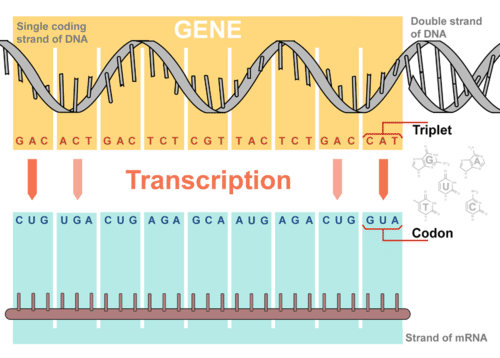



Steps Of Genetic Transcription Biology For Majors I



Replication And Expression Of Genetic Information




Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable




2 6 Dna Rna Structure




Heredity Structure And Composition Of Dna Britannica



Dna Wikipedia




Single Stranded Dna And Rna Origami Science



28 4 Transcription Of Dna Chemistry Libretexts



1



Solved In This Model Of The Central Dogma What Is The Me Chegg Com




Heredity Structure And Composition Of Dna Britannica




Make A Dna Model Amnh




Bio 156 Lab 2 Dna And Rna Journeyoflight79



1



Dna And Rna Basics Replication Transcription And Translation




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks



22 7 Dna Replication The Double Helix And Protein Synthesis Chemistry Libretexts



Structure Of Dna And Rna




Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable




New Dna Rna Tool To Diagnose Treat Diseases Dna Project Dna Activities Dna



Dna Drag And Drop



Dna
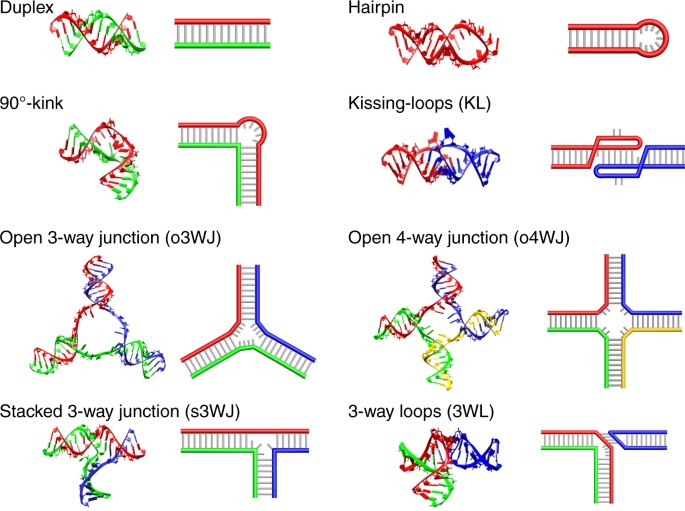



In Vivo Production Of Rna Nanostructures Via Programmed Folding Of Single Stranded Rnas Nature Communications




Flow Of Genetic Information Kit C




Transcription Made Easy From Dna To Rna 19 Youtube



Rna World Wikipedia




The Mechanical Properties Of Rna Dna Hybrid Duplex Stretched By Magnetic Tweezers Biophysical Journal




What Are The Similarities Between Dna And Rna Albert Io
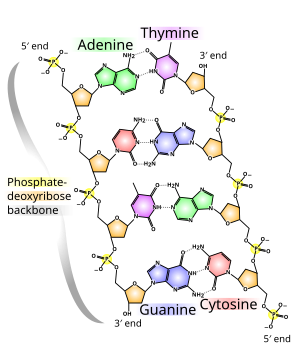



Dna Wikipedia




Dna And Rna Replication
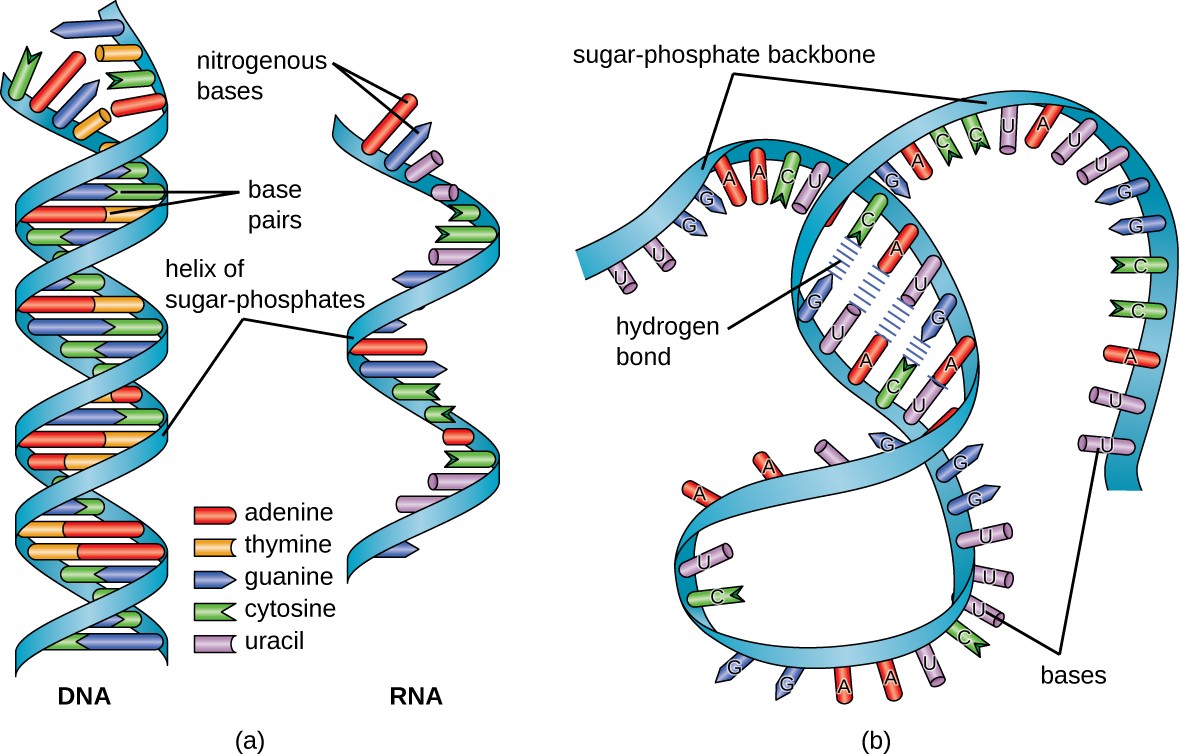



Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology




Bio 156 Lab 2 Dna And Rna Journeyoflight79




Dna Model Made With Tape Colored Straws And Pencils Dna Model Project Dna Project Dna Model
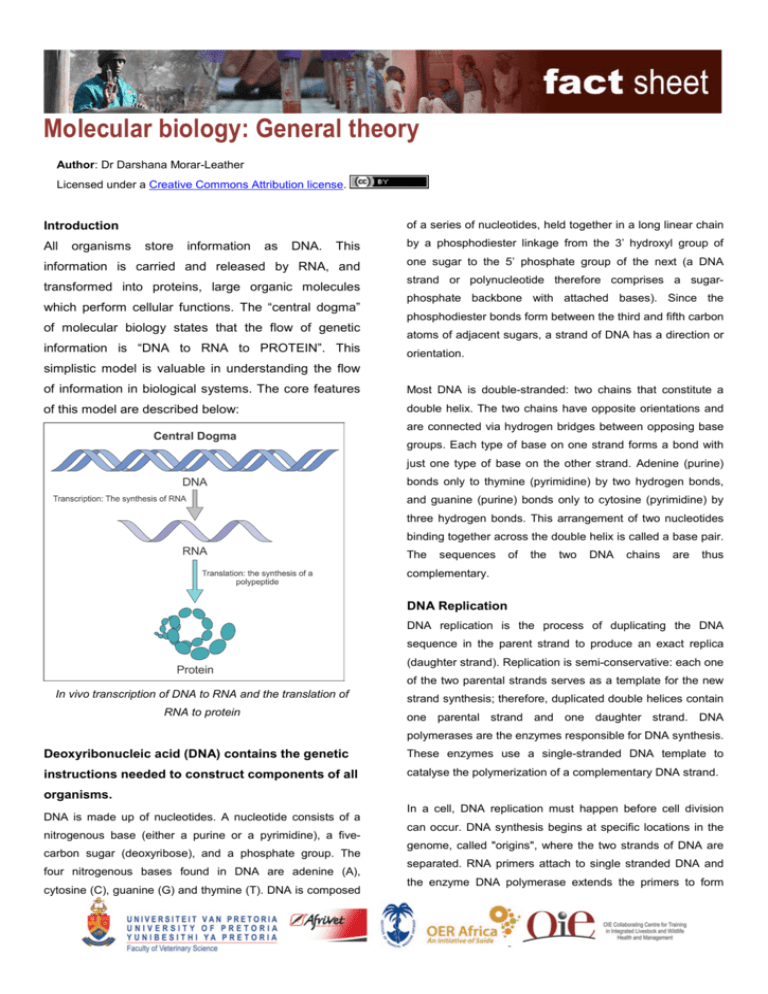



Molecular Biology General Theory




Dna Definition Function Structure And Discovery Biology Dictionary




Dna Replication Microbiology
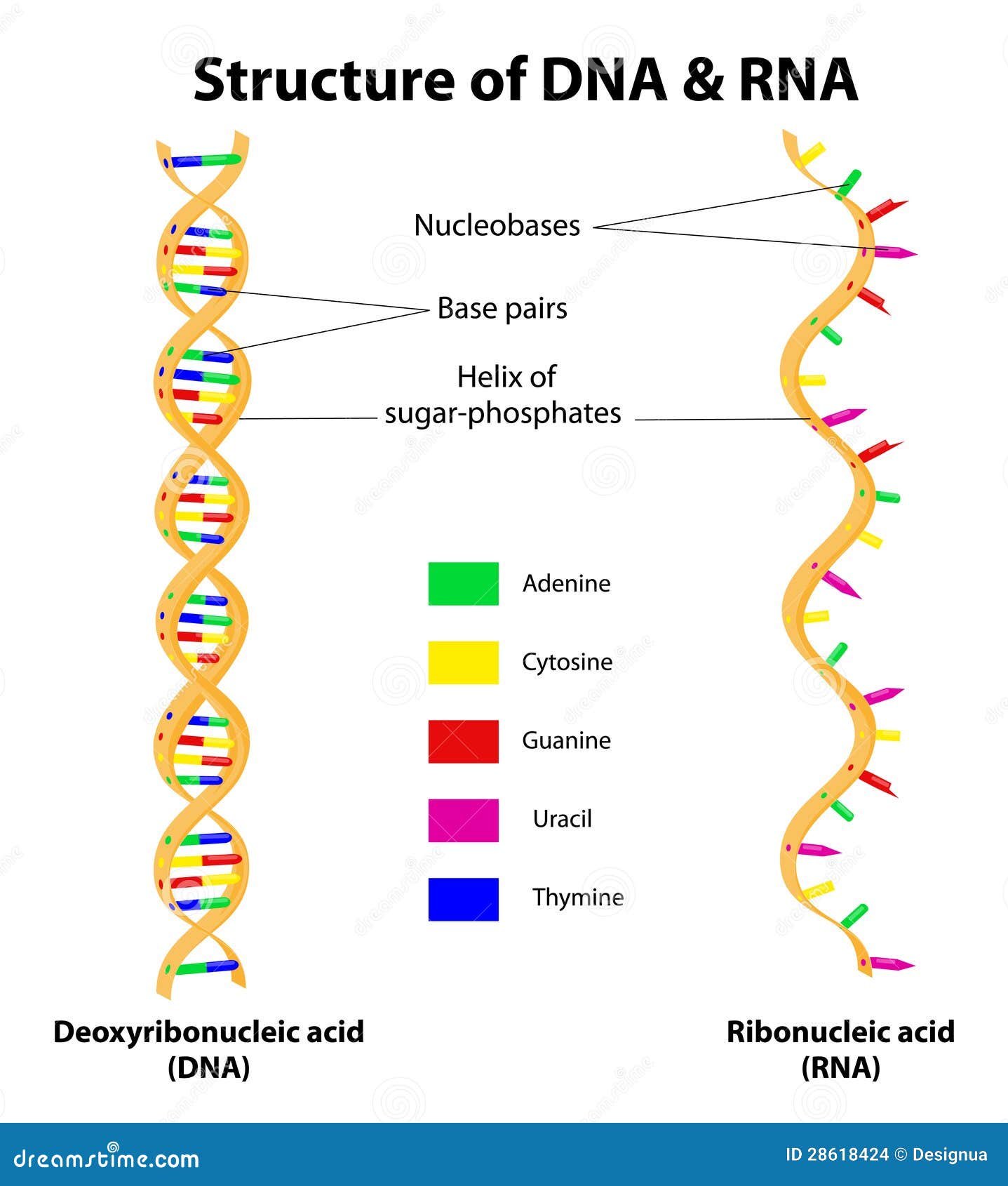



Dna Rna Stock Illustrations 4 661 Dna Rna Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Theoretical Study Of Overstretching Dna Rna Hybrid Duplex
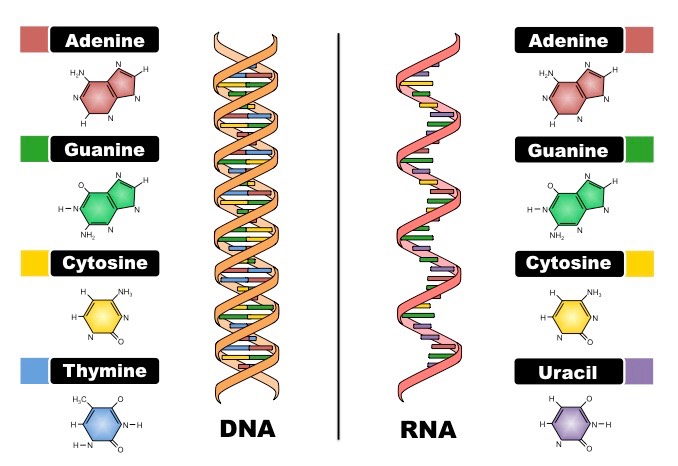



What Are The Structure Of Rna And Dna And How One Might Be Used To Create The Other Socratic




Dna Rna Kit American Printing House




Transverse Current Setup For A Single Strand Dna Or Rna Molecule Download Scientific Diagram



Structure Of Dna And Rna



9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
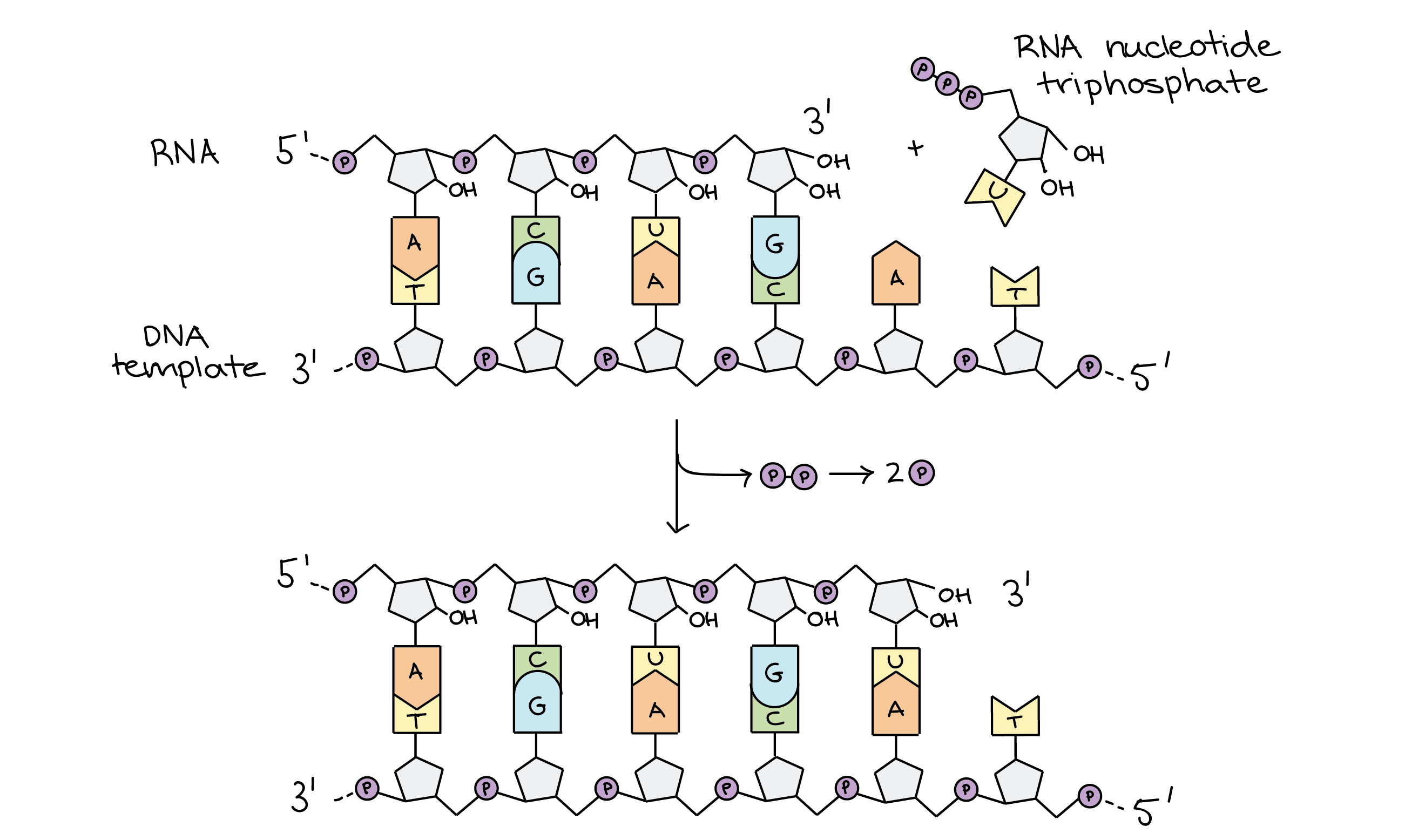



Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna
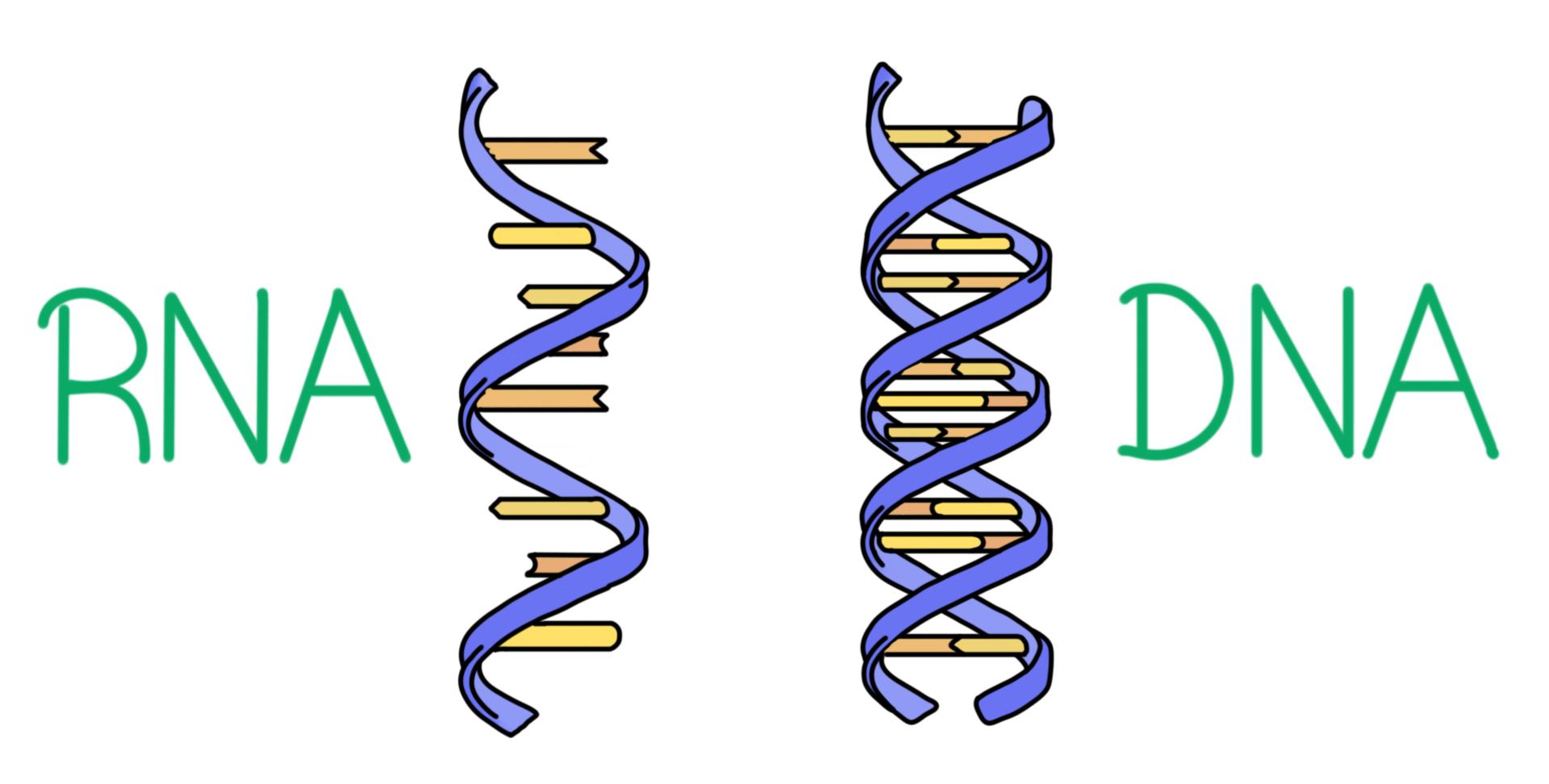



Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii
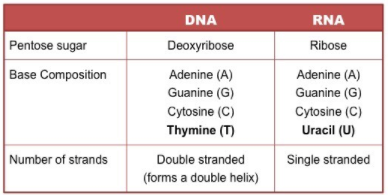



2 6 Dna Rna Structure




Rna Model 24 Bases Minidna Kit Molymod W Biology Supplies Biology Teaching Supplies Genetics Products Dna Models
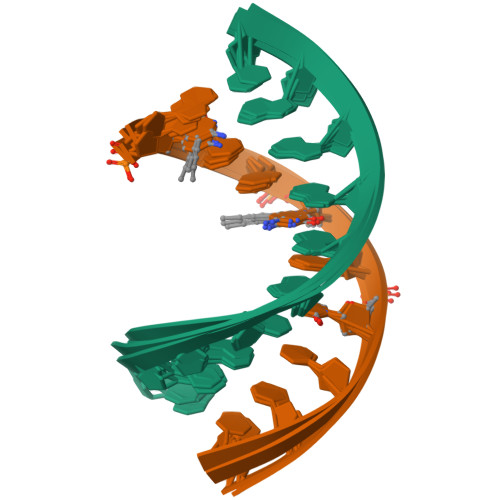



Rcsb Pdb 1oo7 Dna Rna Hybrid Duplex Containing A 5 Propyne Dna Strand And Purine Rich Rna Strand Nmr 4 Structures
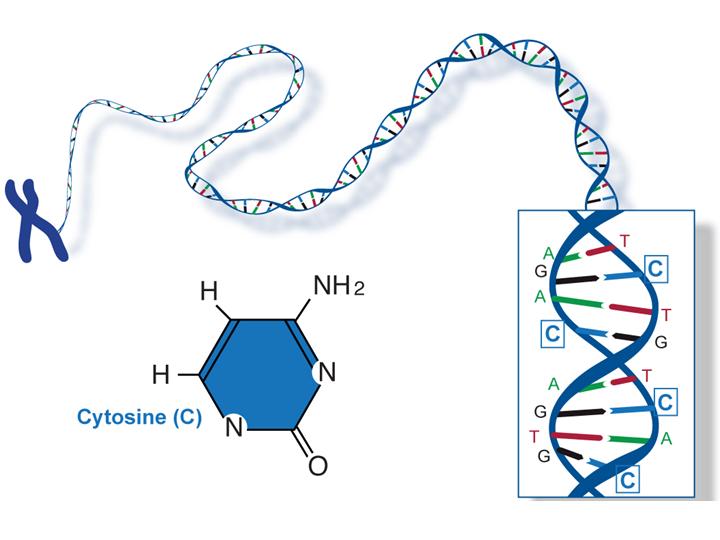



Fact Sheet Dna Rna Protein Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network




Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii
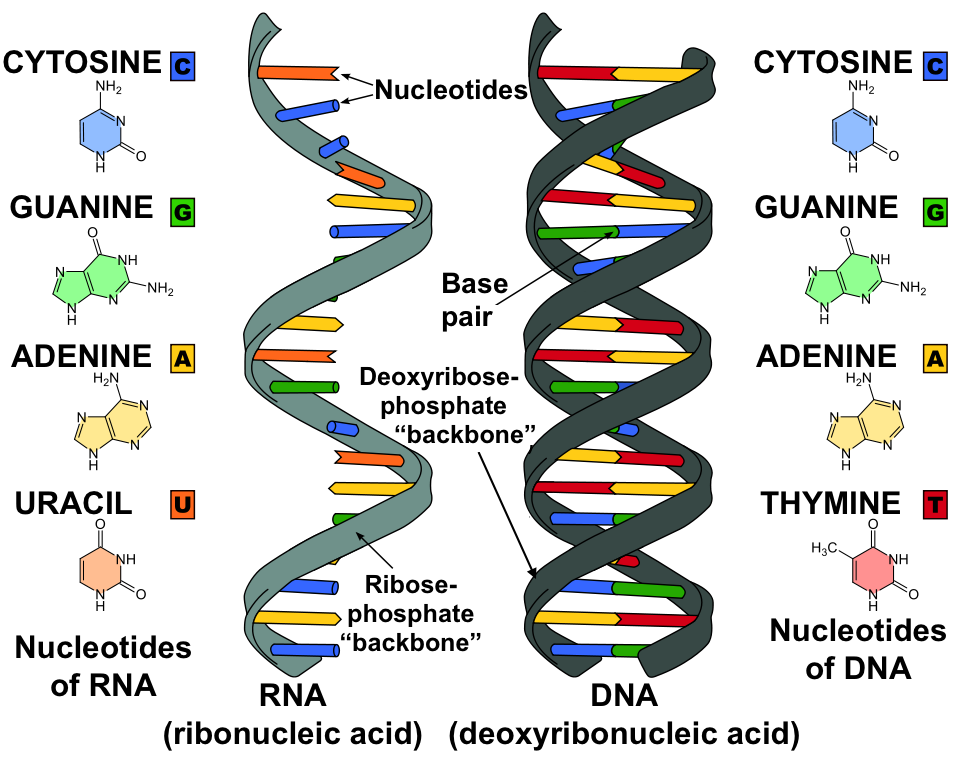



Rna And Protein Synthesis Review Article Khan Academy
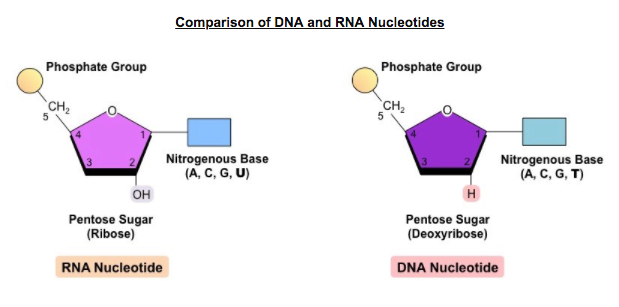



2 6 Dna Rna Structure




Make A Candy Dna Model Youtube




Dna Replication Transcription



9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition



Rna Transcription



Dna To Rna Transcription



コメント
コメントを投稿